Construction
Drilling of the Hydraulic Storage borehole is the main construction challenge. The proposed Hydraulic Storage requires large diameter and deep borehole which is deeper than typical wind turbine drilled monopile shaft.
Impressive Engineering has requested a competent and experienced drilling consultant company to perform a preliminary study on drilling technology and cost estimation of the Hydraulic Storage borehole. The study shows that drilling of Hydraulic Storage large diameter and deep borehole is technically and economically feasible.
Onshore borehole diameter 6 m and depth of 1000 m are already drilled using blind shaft drilling with Reversed Circulation Drilling (RCD). Theoretically, the technology has no limit as far as depth. The feasibility will be more determined by the costs and economical aspects.
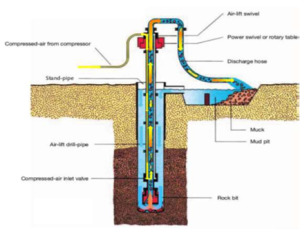
RCD or airlift drilling is proven to be effective up to 5000 m depth. In this technology compressed air is injected into the drill pipe in the annular chamber of the drill bit body above the cutting head. The expanding air-water mixture flows with high speed upwards into the drill pipe and sucks water from the water intake, which is located between the roller cutters of the drill bit body. The cross-flow of water below the cutting head carries drill cuttings to the water intake and subsequently to the surface for disposal by means of a reinforced flexible hose.
A large diameter and deep bore hole can be drilled with two types of drill rigs:
• PBA-type boring machines
• L-type shaft boring machines
Both Drill rigs use reversed circulation drilling.
The Hydraulic Storage bore hole casing functions as a monopile foundation for the wind turbine and therefore the capital cost of the turbine foundation is covered as part of Hydraulic Storage.